Diabetes
Occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or when the cells don’t effectively respond to insulin. This results in an inability to properly control blood sugar levels, which can lead to various health complications over time.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) provides comprehensive guidelines for the management of diabetes. The recommended
treatments for diabetes generally include a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and monitoring. Here are some key aspects of diabetes management that the NIH may recommend:
Medications:
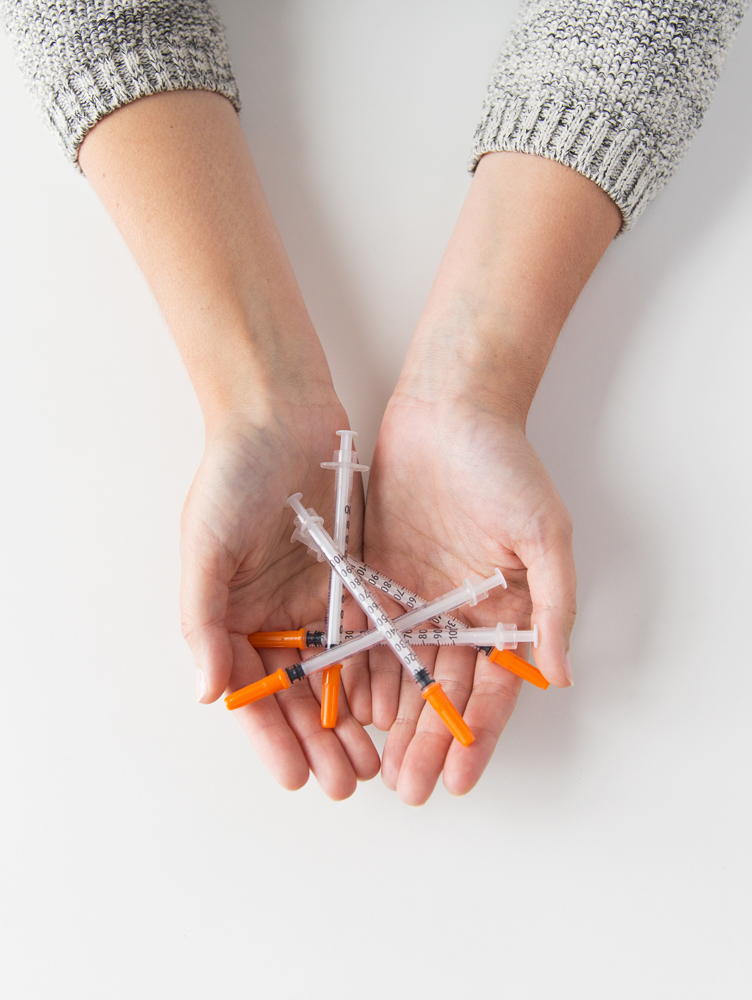
- Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin replacement therapy is typically necessary for individuals with type 1 diabetes, as their bodies do not produce insulin. Multiple daily injections or insulin pump therapy may be recommended.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Initially, lifestyle modifications may be the primary approach. However, if blood sugar levels remain uncontrolled, oral medications such as metformin or other classes of antidiabetic medications may be prescribed. In some cases,
insulin therapy might be required.


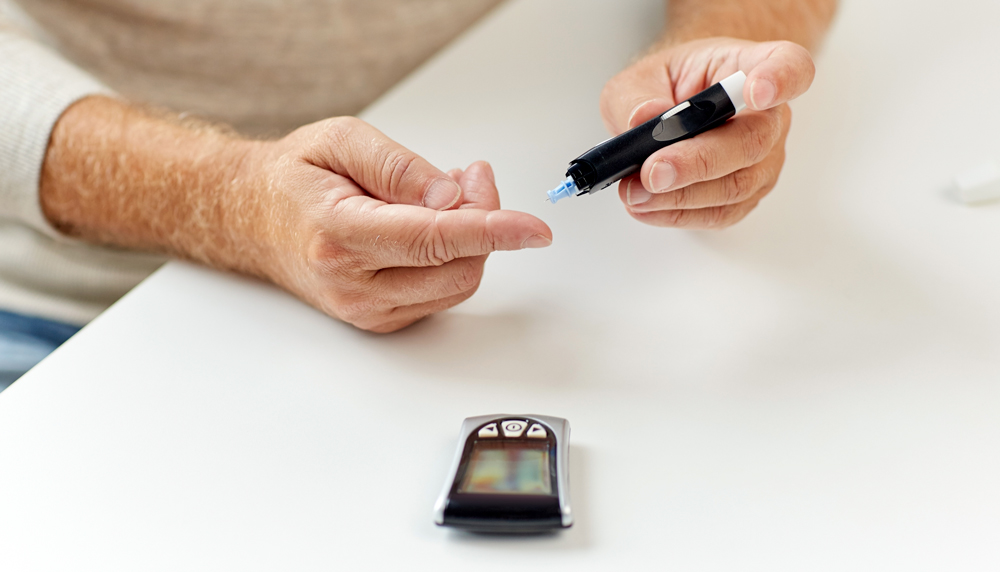
Blood Sugar Monitoring:
-
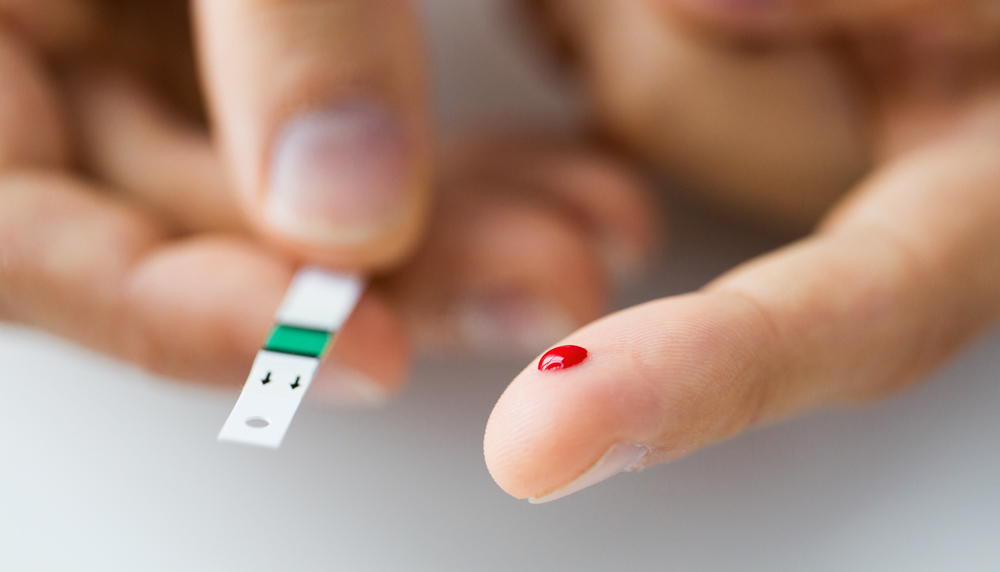
Self-Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels using a glucose meter helps individuals make informed decisions about
medication, diet, and exercise adjustments. -
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): For certain individuals, especially those on intensive insulin therapy, CGM devices may be recommended to provide real-time glucose readings and detect trends.
It’s important to note that diabetes management is highly individualized, and treatment plans may vary depending on factors such as the type of diabetes, the individual’s age, overall health, and other considerations. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to receive personalized guidance and recommendations for managing diabetes effectively.
By implementing a personalized treatment plan that focuses on blood sugar management, lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and ongoing support, an MD can help individuals with diabetes optimize their health and improve their chances of long-term well-being.

